THE PLAN Journal (TPJ) is an open, inclusive, non-ideological and independent platform, founded on an ongoing praxis of criticality. The journal aims at disseminating and promoting innovative, thought-provoking and relevant research, studies and criticism in architecture, design and urbanism. In addition, the TPJ wants to enrich the dialog between research and the professional fields, in order to encourage both applicable new knowledge and intellectually driven and locally relevant modes of practice. With an overarching concern for recognizing quality research, the criteria for selecting contributions will be: innovation, clarity of purpose and method, and the potential transformational impact on disciplinary fields or the broader socio-cultural context.
Latest Articles
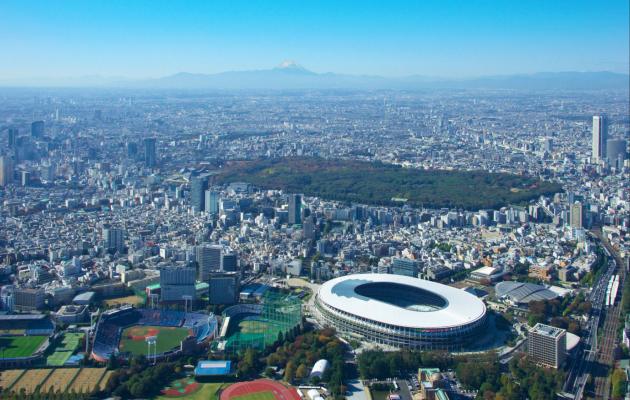
The Japan National Stadium: Between Architectural Bigness and Urban Smallness
VOLUME 9/2024 - Issue 1 , Pages: 1 - 21 published: 2024-06-19In 2012, Zaha Hadid Architects (ZHA) was announced winner for the competition to design the Japan National Stadium, the main venue for the 2020 Olympics. Over the years, the project faced a range of controversy that ended with the scrapping of ZHA’s proposal in 2015, and the adoption of a non-iconic stadium designed by Kengo Kuma, one that is more integrated with its context. The critique against ZHA’s project involved Japanese architects led by Fumihiko Maki; it stemmed from the urban consequences such an architectural object would have, bringing the protagonists into conflict at the very intersection of their nature as architects and urban planners. This paper aims to analyze the reasons behind this controversy, which lies within the theoretical debate between a phenomenological approach on one hand and the autonomy of design on the other. Despite her established status as an archistar, Hadid’s proposal seemed to suffer the side effects of Koolhaasian “bigness”; the heritage discipline of preserving the built and natural environment of the neighborhood suddenly became a matter such an important structure had to deal with.
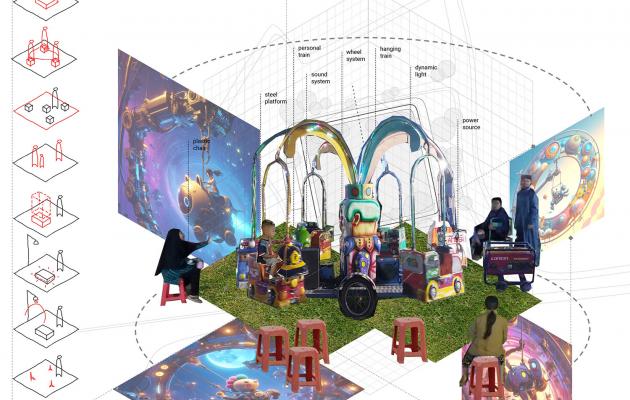
Object as Portal: Actual-Virtual Multi-Space of Temporary Urban Games Space
VOLUME 9/2024 - Issue 1 , Pages: 1 - 24 published: 2024-06-17This study proposes utilizing AI text-to-image technology to project virtual multi-space onto the spatial operations of actual objects. The foundation of this research lies in demonstrating multi-space within urban game spatial practices. The interplay between actual and virtual notions of space recalls the multi-space concept. The actual-virtual relationship is infinite, potentially giving rise to virtual entities mirrored through spatial mechanisms and operations. Alun-alun, a public space in Indonesia, undergoes everyday time-based temporal-spatial alterations. Notably, it transforms into an imaginative game space at night. By constructing temporary spaces with simple game objects and mechanisms, we observe the potential for multi-space presence based on spatial operations. Generative AI, particularly text-to-image operations in architecture, can project game objects and their properties, revealing various virtual, imaginative multi-space alterations. The study’s findings contribute to expanding spatial design methods in architecture, envisioning collaboration between multi-non-physical spaces within the actual-virtual framework in a future digital realm.
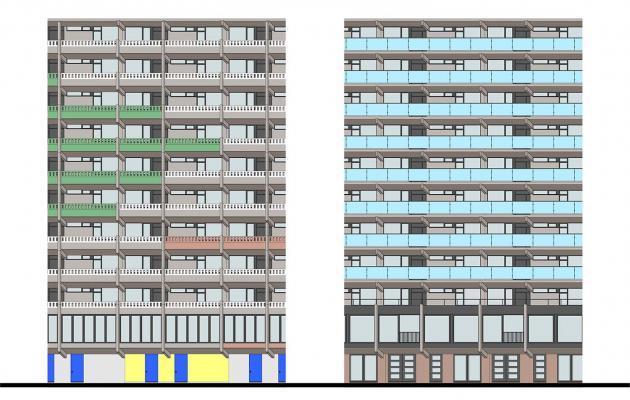
Fine-Tuning the Intensity of Modifications to Revitalize Brutalist Mass Housing: Learning from Park Hill and Bijlmermeer
VOLUME 9/2024 - Issue 1 , Pages: 1 - 26 published: 2024-06-28This essay investigates design opportunities associated with the revitalisation of Brutalist mass housing megastructures. Through a comparative analysis of two sets of projects – one pair in the Park Hill Estate (Sheffield, UK) and one pair in the Bijlmermeer district (Amsterdam) – the text theorizes an implicit process where intensity of modification is honed from one experience to the next. This process responds to the need for change brought by new social, spatial, environmental, and figurative requirements while simultaneously addressing conceptual and material integrity issues of these controversial architectures. The essay takes as its starting point the dilemmas ideally present in a practitioner’s mind when adopting an inventive approach to modifying these buildings, overcoming a purely conservative mindset. Following a reflection on possible actions, it emphasises four lessons derived from four design themes: the ground floor as a link between building and city; inner circulation as a relational experience; dwelling interiors as variable spaces; and façade design as a means of expressing change. The reflections thus offer interpretative and operational contributions to imagine actions for similar housing structures.
The Wisdom of Cultural Mapping in Reparative Planning — City in the Woods: Mapping of Cherokee Village, Arkansas
VOLUME 9/2024 - Issue 1 , Pages: 1 - 31 published: 2024-06-14As communities and design professionals confront complex cultural issues in planning, new tools are needed to introduce interdisciplinary cultural inquiry into urban design/planning. Reparative planning is premised on a reckoning with socio-economic and environmental decline through design of the built environment. Cultural mapping is necessary to both visibilize suppressed narratives behind decline and inequity, as well as underwrite new policy and development approaches. City in the Woods is a cultural mapping project that supports planning for Cherokee Village. Moving beyond the map as object to mapping as a process, we employed the deep map to sketch a memoir of place different from the disciplinary linearity found in conventional cartography. Cultural mapping animates diverse data sets through various visual literacies ranging from serial filmstrip narratives, to collages, thick description drawings that reconstruct lost local heritage landscapes, and geospatial mapping of the built environment. Change requires storytelling. This descriptive agency in planning, entailing collaboration between design professionals and community, models an equity-based approach beginning with stories that enable community self-advocacy, motivate institutional redesign, and construct new urban forms.
Unkapani Upcycle: Cultivating Grassroots Enterprise and Urbanism in Istanbul
VOLUME 9/2024 - Issue 1 , Pages: 1 - 16 published: 2024-06-13Pervasive environmental and social crises necessitate the invention of new models for conceptualizing architecture. In pursuit of a more sustainable and equitable paradigm, our research lies at the intersection of social equity through community engagement, the adaptive enhancement of architecture and urban fabric, and sustainable practices centered on the salvage and reuse of materials and infrastructure. Our research questions are prompted by this same approach: can the emergent conditions and needs of a fully contemporary project help inform its expression, use, and cycle of life in more advantageous ways than the two positions above? How might we structure an a posteriori methodology that allows for flexible project-making alongside the changing conditions of buildings in time? The current locus for our research is the city of Istanbul, a metropolitan region unique in its historical, cultural, and political contexts, yet simultaneously representative of pervasive social, economic, and environmental conditions in cities across the globe.
Featured Articles
AI Time, Timing, and Timelessness
VOLUME 8/2023 - Issue 2 , Pages: 207 - 213 published: 2024-01-12The Right to Housing: A Holistic Perspective. From Concept to Advocacy, Policy, and Practice
VOLUME 7/2022 - Issue 2 [The Right to Housing], Pages: 269 - 267 published: 2023-01-10Baukultur in a Cybernetic Age: A Conversation
VOLUME 6/2021 - Issue 1 , Pages: 7 - 28 published: 2021-05-14We received and we gladly publish this conversation among distinguished theorists and scholars on an important topic, also aligned with the cross-disciplinary mission of our journal. [MS]
ABSTRACT - The article offers a multi-author conversation charting the future of architecture in light of the apparent tension between Baukultur, which combines the culture of building and the building of this culture, and the rapid changes brought about by digital technology, embracing cybernetics and artificial intelligence. The article builds on a discussion of Baukultur to debate in what sense buildings are “machines for living in,” then examines neuromorphic architecture wherein cybernetic mechanisms help buildings sense the needs of their occupants. It closes with an example of a building complex, Kampung Admiralty, that combines cybernetic opportunities with a pioneering approach to building “community and biophilia” into our cities. This article interleaves an abridged version of Michael Arbib’s (2019) article “Baukultur in a Cybernetic Age,” 1 with extensive comments by the co-authors.
Gender Matters. The Grand Architectural Revolution
VOLUME 4/2019 - Issue 2 [GENDER MATTERS], Pages: 273 - 279 published: 2020-02-07Japanese Architecture Returns to Nature: Sou Fujimoto in Context
VOLUME 7/2022 - Issue 1 , Pages: 7 - 36 published: 2022-05-16We received and we gladly publish a contribution by distinguished author Prof. Botond Bognar. [MS]
ABSTRACT - The essay introduces the development of Sou Fujimoto’s architecture as it has been influenced by various sources and experiences leading to his recently completed and highly recognized major project, the House of Hungarian Music in Budapest. Among these influences the contemporary economic and political conditions in Japan and beyond, as well as the nature-inspired work of prominent Japanese designers are discussed. Touching upon the seminal work by Tadao Ando and Toyo Ito, the essay also highlights the contrasts and occasional similarities between the so-called “White School” and “Red School” in contemporary Japanese architecture, in referencing nature as the primary source of their designs. Today, these “schools” are best represented, respectively, by the activities of SANAA and Kengo Kuma. Although Fujimoto’s architecture is clearly derivative and part of the radically minimalist White School, the House of Hungarian Music reveals an intimacy and richness
in articulating its relationship to the surrounding natural environment, which quality, if perhaps momentarily, points beyond the minimalism of the “Whites.”